Los Cedros Reserve to be protected from mining after comprehensive Ecuador Constitutional Court ruling on Rights of Nature and the environment

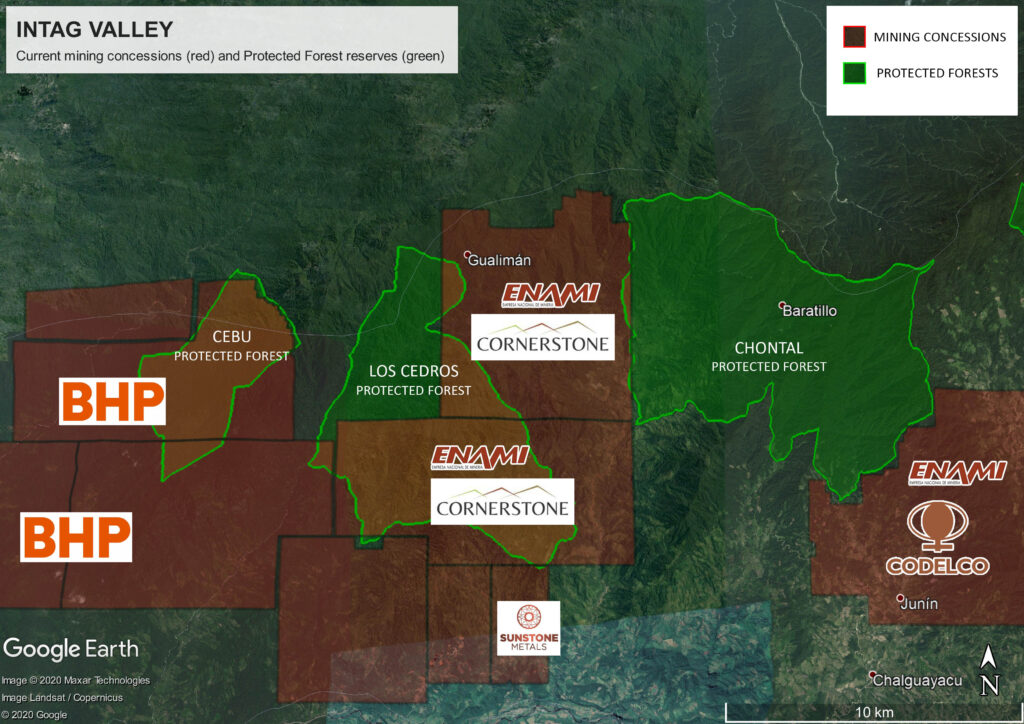
In a significant ruling on December 1, the Ecuador Constitutional Court revoked the water and environmental rights of Cornerstone Capital Resources and the Ecuador state mining company (ENAMI) for the Rio Magdalena concessions that cover most of the internationally renowned Los Cedros Reserve.
The ruling sets an important precedent for Ecuador, which was the first country in the world to enshrine the rights of nature in its rewritten constitution in 2008.
“The Court stated that the companies had been responsible for a number of constitutional violations. These included violating the rights of nature, the rights of nearby communities to clean water and environment and the rights of communities to consultation over the mining projects. In addition, the Court ruled that the companies failed to acquire adequate environmental and water permissions pertaining to the extraordinary diversity and vulnerability of the region,” says Liz Downes from the Rainforest Action Group, an advocacy and research group investigating the actions of Australian mining companies in Ecuador.
The Court also ordered the government to adopt regulations so that future environmental licenses and water licenses for mining and other extractive industries do not risk violating the Rights of Nature.
“This order could become a precedent to protect significant water sources and other Protected Forests. There are 2.4 million hectares of Protected Forest in Ecuador currently at risk due to large scale mining,” says Liz Downes.

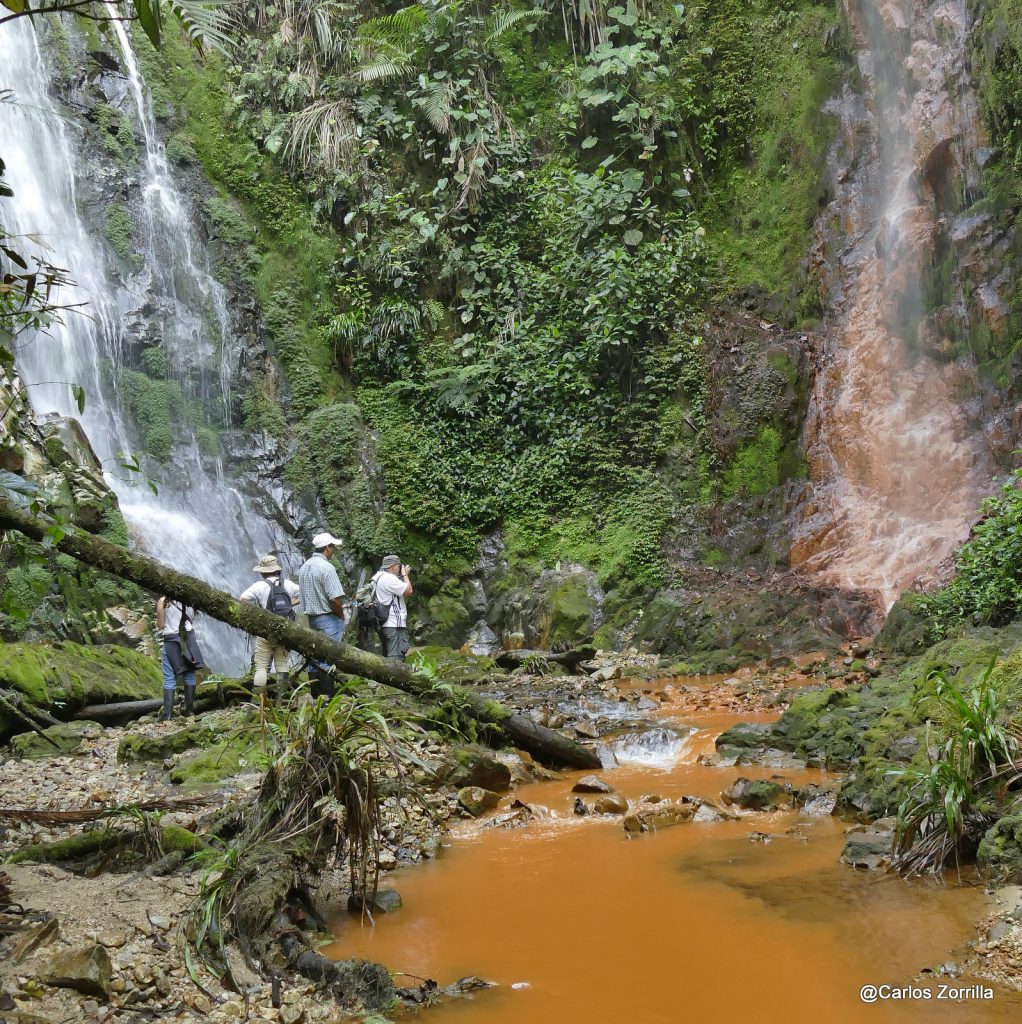
“Mining activities – even at early exploration stage – in the high-altitude cloud forests and grassland regions of the Ecuadorian Andes risk contaminating and depleting the water sources of local communities and the farms they depend on, as well as risking the extinction of thousands of endemic and endangered species. Across Ecuador, communities on the frontline say they have never been consulted about mining, and this ruling potentially gives weight to their argument, ” says Liz Downes.
Around 30% of mining concessions in Ecuador granted by the government since 2017 – just over 700,000 hectares – are owned by Australian companies, who are exploring for copper and other base metals. Mining companies potentially impacted by the ruling include SolGold, who are developing 13 priority projects nearly all of which cover protected areas.
Hanrine (Hancock Prospecting) and BHP each have several concessions in the region around Los Cedros in north-western Ecuador, which almost without exception overlap the buffer zones of mega-biodiverse and threatened forests like Los Cedros and Cotacachi-Cayapas National Park. Communities in this area have strongly resisted mining for decades.
Cornerstone Capital Resources, in a press release, says it has made a submission to the Constitutional Court requesting further details about the impact of the ruling on its activities.
“It is unclear as yet as to how the ruling will be enforced in terms of legislation. But this is set as a precedent case with no legal appeal possible,” says Liz Downes.
A plan to manage and care for Los Cedros Reserve will be established jointly with the Ministry of the Environment, Water and Ecological Transition, residents of the neighbouring communities, local and state councils, as well as researchers, scientists and academics who have conducted studies in the Protected Forest. In accordance with the ruling, this process is to be overseen by the Ombudsman's Office.
FULL RELEASE HERE